Artificial intelligence (AI) in practice And Use Cases For AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become a famous catchphrase in almost all discussions about technology. Autonomous cars, buses and planes, drones, robots, connected traffic management, smart cities, predictive maintenance, and so on – these are just some of the use cases we associate with AI.
At first glance, many of them seem like science fiction. Nevertheless, AI has long since arrived in our everyday lives.
Machine learning can be monitored or unsupervised.
Machine learning summarizes some learning algorithms, which are divided into five categories according to the type of learning used: supervised, unsupervised, partially supervised, and reinforcement learning, and finally, learning through transfer.
Machine learning requires structured and categorized data. Only with them is a system able to learn how new and similar data can be classified. A human expert can accompany the training to improve performance.
This continuously analyzes the system, shows it the correct categories, and corrects it in the event of incorrect classifications.
Deep learning has its roots in the early 2010s and is a sub-category of machine learning. It is based on the unsupervised learning methodology.
Deep learning systems, on the other hand, do not require any structured data. You can determine the distinguishing features yourself.
With the help of deep learning, the system can identify the distinguishing features of the data itself without human experts having to do a prior classification.
Technological advancement creates many use cases for AI.
In recent years, the development of these various machine learning methods has flourished thanks to a favorable environment coupled with the continued decline in the price of computing power and the dramatic increase in the flow of data from social networks and devices.
The use of AI technologies, therefore, appears suitable for many applications. Because more and more often, large amounts of heterogeneous data are available, even almost in real-time.
Advances in artificial intelligence technologies are providing us, humans, with new tools to make decision-making and performing specific tasks easier.
In the following, we list some examples from professional and everyday life in which artificial intel Online shopping and advertising ligence is already used today:
– Artificial intelligence is widely used to provide personalized recommendations to users and customers based on their search history, previous purchases, or browsing habits. AI is becoming increasingly important in the world of commerce.
The interests and expectations of visitors to an e-commerce site are assessed based on their data: is it a woman or a man? Parents? To people who are used to buying sportswear? Or a person who prefers comfortable clothes or luxury clothes? .
The system has tracked your online activities and learned from them to make you a targeted offer. Products that you browse on various shopping sites or search engines will be tracked, and you will be served advertisements related to these products.
Data science techniques and behavioral analyses provide existing tools in companies with technological modules for this type of personalization.
Smartphones and social networks –It seems like a challenge to imagine our life without cell phones. Our daily lives can no longer be imagined without the wide range of possible uses for our cell phones.
Some of these applications are based on AI. The intelligent assistants built into our phones like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant are the most prominent examples.
Mobile technology platforms are developing their own AI solutions to automatically monitor and manage the various aspects of their devices, such as battery management.
Even with social media apps such as Facebook, Twitter, or Instagram, AI controls your news feed, which you see while surfing on these platforms, or the notifications you receive. Your tastes and preferences,
Personal digital assistants, voice control, and automatic input – smartphones use artificial intelligence to deliver products that are as relevant and tailored to you as soon as possible.
Virtual assistants answer the questions, provide suggestions and help with everyday tasks. On your mobile device, for example, the integration of AI makes typing more convenient.
It can predict the words, phrases, and emojis based on your general usage and writing style. This goes beyond previous approaches to automatic text recognition.
The AI learns step by step to imitate your writing style and recognize the specific context. As time goes on, she gets better and better at it.
Smart Home – When using AI in innovative home development, we naturally think of Alexa and Bixby. However, these AI applications are not limited to these intelligent voice assistants.
The system saves electricity by automatically switching the light on and off and intelligently operating other household applications. These are apps that use artificial intelligence to make the home more intelligent.
The artificial intelligence used is constantly evolving. Evermore sophisticated solutions are being developed to understand our behavior and act accordingly.
Security Surveillance – The idea of artificial intelligence brought the concept of its use for surveillance on a larger scale. The ethical limits for the use of AI are hotly debated in this area in particular; however, there can be no doubt that AI will gradually take hold here as well.
Monitoring continuous streams generated by many cameras and other devices is tedious for people and reaches their recording limits. With face, object, and location recognition technologies, an AI can guarantee continuous monitoring and thus security.
Financial Services – Banking is one of the areas where technological inventions are introduced earlier than most.
AI applications help banks in many areas, such as recognizing fraudulent activities, analyzing trends in customer investments, increasing the security of digital bank accounts, proposing attractive financial products and investment opportunities, or offering better customer service.
Medicine and Health – Thanks to advances in machine learning, deep learning, and big data, artificial intelligence is gradually changing the world of medicine.
AI is used in the areas of surgery, radiology, drug development, and hospital management. The advancement in artificial intelligence will make the medical diagnosis of certain diseases more precise and detailed.
Large amounts of data can now be captured more easily, quickly, and efficiently thanks to big data.
For example, researchers with experience in data analysis and data science have developed new methods to combat the spread of the coronavirus. For example, artificial intelligence is used to study vaccines and treatments for the disease.
Not to mention, artificial intelligence enables the fight against Covid-19 by being used to produce thermal images and in other situations at airports.
AI can use a CT scan of the lungs to determine whether an infection is present or how far it has progressed in the hospital. The collection of data to track the course of the infection has also been made easier thanks to AI.
The advancement of AI and big data goes far beyond the advancement of medical diagnostics. The surgery, radiology, and therapy branches will be redesigned shortly.
The main goal is to improve the accuracy of the treatment and prevention of various diseases that affect the world’s population.
Researchers are currently investigating how artificial intelligence can analyze large amounts of health-related data to uncover recurring patterns, gain new knowledge and improve personal diagnosis for patients.
Here is an example: Researchers have developed an artificial intelligence program that can respond to emergency calls. The program is expected to identify cases of cardiac arrest on calls faster and more frequently than medical dispatchers.
Another example is the EU co-funded the KConnect project, developing multilingual search and text services to help people find the medical information that best suits their needs.
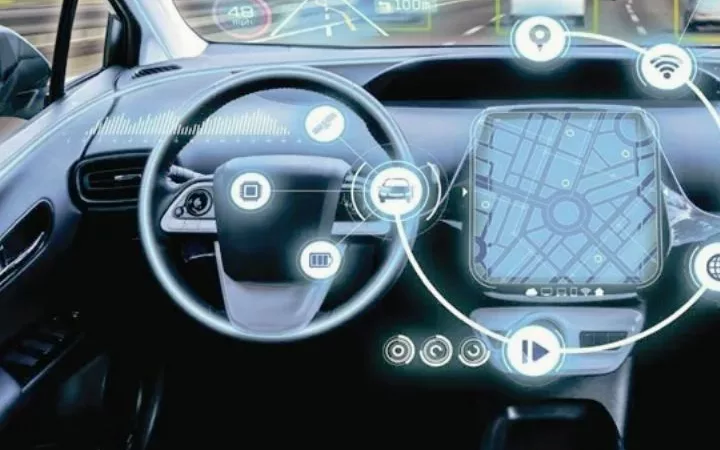
Automotive – Connected Cars are another area where artificial intelligence is becoming increasingly important and prevalent in our daily lives.
Not only companies like Tesla are pioneers in automotive automation applications. Many automakers are also considering integrating artificial intelligence into cars to provide services to drivers.
Information is shared and communicated between cars to be able to drive better in traffic. Real-time updates of traffic entrances and roadblocks are transmitted immediately to remind other vehicles in the network to allow a detour.
While self-driving cars have not yet become the norm, our cars have already used AI-based safety features without using machine learning or deep learning.
For example, automatic emergency braking (AEB) is a device that enables the car or truck to brake automatically if an impending collision with a recognized vehicle, pedestrian, or other obstacle is detected.
The AEB system is designed for various road scenarios. First, the driver is warned of obstacles in front of the car. The AEB system automatically brakes at different levels according to the intelligent speed algorithm if the driver doesn’t respond to avoid the collision.
In addition, other intelligent functions such as automatic parking, voice control, gesture control, and fatigue detection are on the rise.
Aviation – In the aerospace industry, AI can provide automatic communication with control towers, automatic take-off and landing of aircraft, automatic routing of aircraft ashore, and fault detection inspections (predictive maintenance).
AI enables airlines to increase their revenue by quickly understanding customer preferences, optimizing prices in real-time, and determining preferred travel destinations for specific target groups; to use the airspace optimally through predictive maintenance; tracking baggage volume in real-time to accurately estimate the amount of fuel required for the flight and reduce costs; to increase customer satisfaction through critical figures of the travel experience or the travel route; Risk management models and strategy by integrating the fatigue estimation model into the crew planning software. Therefore, the schedule can be adjusted based on each pilot’s estimated risk of fatigue.






